Preprocesar datos
Preprocesamiento
Modelos basados en árbol
|
Modelos "mutiplicativos"
|
|
| Variable Categórica Ordinal |
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Variable Numérica |
Nada |
|
| Texto | CountVectorizer, TfidfVectorizer, HashingVectorizer, Word embeddings | |
from sklearn import preprocessing, compose
x_preprocessing_tree = compose.ColumnTransformer(transformers=[
('cat', preprocessing.OrdinalEncoder(), cat_vars),
], remainder='passthrough')
x_preprocessing_mult = compose.ColumnTransformer(transformers=[
('cat', preprocessing.OneHotEncoder(), cat_vars),
('num', preprocessing.StandardScaler(), num_vars),
], remainder='drop')
Variables numéricas
TO-DO: Scaling and Normalization
RankGauss (aka QuantileTransformer)
Its based on rank transformation.
- Assign a linspace to the sorted features from 0..1,
- Apply the inverse of error function ErfInv to shape them like gaussians,
- Substract the mean.
This works usually much better than standard mean/std scaler or min/max.
RankGauss = QuantileTransformer(n_quantiles=100, random_state=0, output_distribution="normal")
Variance Threshold
- VarianceThreshold is a method of feature selection.
- It removes all features whose variance doesn’t meet some threshold.
Map data to a normal distribution: Box-Cox
A Box Cox transformation is a generic way to transform non-normal variables into a normal shape.
| Lambda value (λ) | Transformed data |
|---|---|
| -3 | Y⁻³ = 1/Y³ |
| -2 | Y⁻² = 1/Y² |
| -1 | Y⁻¹ = 1/Y¹ |
| -0.5 | Y⁻⁰·⁵ = 1/√Y |
| 0 | log(Y) |
| 0.5 | Y⁰·⁵ = √Y |
| 1 | Y¹ |
| 2 | Y² |
| 3 | Y³ |
Categorical features
| Ordinal Encoding o Label Encoding | One-Hot Encoding |
|---|---|
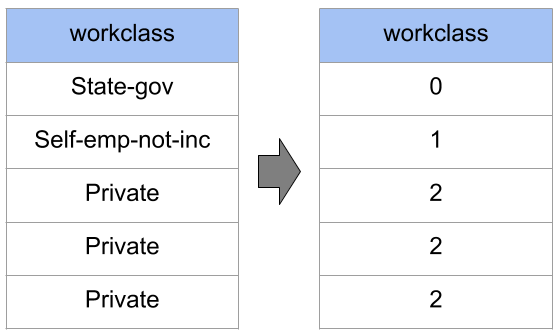 |
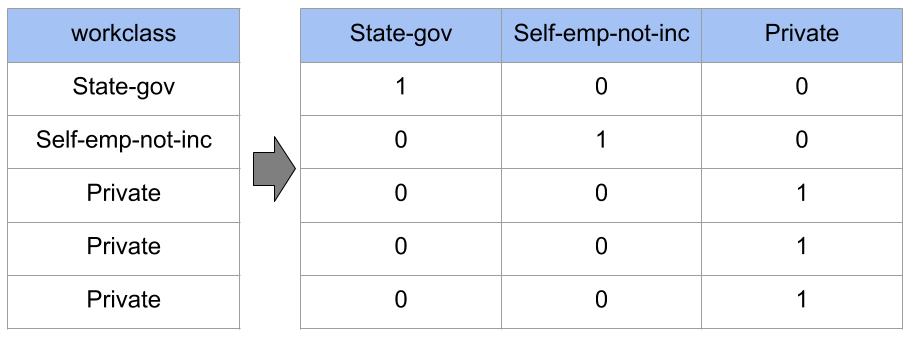 |
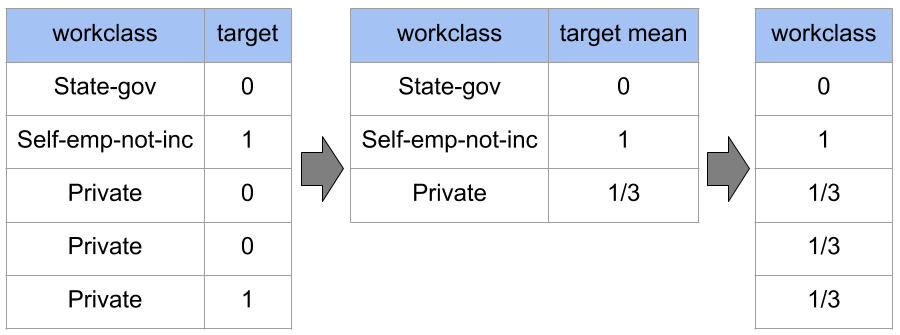
Target Encoding o Mean Encoding
Ingeniería de características = CREATIVIDAD + CONOCIMIENTO DEL DOMINIO
La ingeniería de características (Feature Engineering) es la generación de nuevas características en base a las ya existentes. Esto facilita el trabajo a nuestros modelos.
- Si tienes el precio de la casa y los metros cuadrados, puedes añadir el precio del metro cuadrado.
- Si tines la distancia en el eje x e y, puedes añadir la distancia directa por pitagoras.
- Si tines precios, puedes añanir la parte fraccionaria pq es muy subjetiva en la gente.